Bladder cancer is caused by the uncontrollable growth of urinary bladder cells. Over time these cell growths invade the bladder’s healthy tissue and form tumors. Some bladder tumors can appear due to metastasis, where the cancerous tissue gets transferred from nearby organs. According to The American Cancer Society, approximately 80,470 people in the United States will be diagnosed with bladder cancer in 2019.[1] Considering the magnitude of the situation, here are some basic fact that can prepare you for the worst.
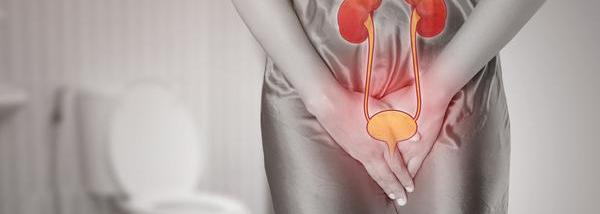
Common Warning Signs
Early-stage bladder cancer can be tricky for doctors to diagnose. Most small tumors don’t cause any discomfort or pain, so they are challenging to locate.
Here are the most common indicators of early-stage bladder cancer[2]:
- Blood in your urine
- Pain during urination
- Frequent or uncontrolled urination
Advanced Warning Signs
Bladder cancer symptoms will become more evident as the disease progresses. Late-stage bladder cancer can be excruciating and uncomfortable.
The symptoms of late-stage bladder cancer may include[3]:
- Lower back pain
- Difficulty urinating
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Feeling weak
- Swollen feet or legs
- Bone pain
- Abdominal pain
- A persistent, unexplained cough
- Jaundice, or the yellowing of your skin
These symptoms are a sign that your cancer has progressed past the early stages, and the treatment will be more difficult. Patients who have late-stage bladder cancer can go into remission, but you’ll need to have a team of qualified medical professionals guiding your treatment.
Bladder Cancer Diagnosis
There are dozens of tests your doctor can do to determine if you have bladder cancer. The most reliable method is a urine test. If your doctor discovers any blood in your urine, he should immediately order a urine cytology test. The cytology test will reveal if there are any tumor cells present in your urine. We recommend that you also get a cystoscopy. Your doctor will be able to look inside your urethra and check for tumors by inserting a small, flexible tube. The last step in the diagnosis involves a biopsy of your bladder tumor and bladder muscle to see how far cancer has spread. You can also get different scans to see if there are any metastasis to other parts of your body.
Bladder Cancer Treatment
Some bladder tumors can be surgically removed. Some male patients may have to get a radical cystectomy. The doctors will remove the entire bladder, and sometimes even the prostate and urethra. For women, the surgery may involve removal of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and partial removal of the vagina. Some patients will have to carry a urine bag after the surgery. The alternative to surgery is treating cancer with chemotherapy. Other forms of therapy can involve the use of radiation or boosting your immune system.
Tips for Bladder Cancer Patients
Patients diagnosed with early-stage bladder cancer have a very high recovery rate. If you have any reason to believe you have bladder cancer, immediately consult your physician. After getting tested, you can plan your course of treatment with your doctor. Many experts suggest improving your diet to fight the disease.[4] The Gerson Diet has proven to be succesful in battling cancer by consuming fresh fruit and the use of coffee enemas.[5]
[1]https://www.cancer.org/cancer/bladder-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
[2]https://www.cancer.gov/types/bladder/patient/bladder-screening-pdq
[3]https://www.cancer.gov/types/bladder/patient/bladder-screening-pdq
[4]https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5842847/
[5]https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/cam/patient/gerson-pdq


